Quick Commerce (Q-commerce) | Basics
A deep dive into India's Quick Commerce Ecosystem: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Hello,
Commerce has always been a constantly evolving space. Many new types of commerce have evolved in the last few years…online commerce, social commerce, modern commerce, live commerce, etc. Every new technology tries to lay its impact on this space. With each disruption, it looks like space will completely change but that has not happened yet. Each new type of commerce just establishes its own share.
Quick commerce is the latest disruption in this space. The value it is able to generate lies in the feeling of receiving the product instantly in 10 minutes. In this article, we will deep dive into India's Quick Commerce Ecosystem: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities. Happy reading!
Garvit Sahdev enjoys understanding ideas that shape our world. The Thoughtful Tangle is an initiative to share this journey and experience with his friends who love to do the same. He selects one idea and dives deep into it to understand its basics, relevance, impact and opportunities around it. The thoughtful tangle is special because 👇
📝 One long article per idea. We call it ‘The Basics’.
📝 Multiple unique insights. Separate small articles for special ‘Insights’.
🧑🤝🧑 Experts perspective. Check out ‘Insiders’
We are doing a series on ‘Quick Commerce’ as it is truly an idea which is shaping Indian commerce in many ways. Check out this series at
» The Quick Commerce Series | The Thoughtful Tangle
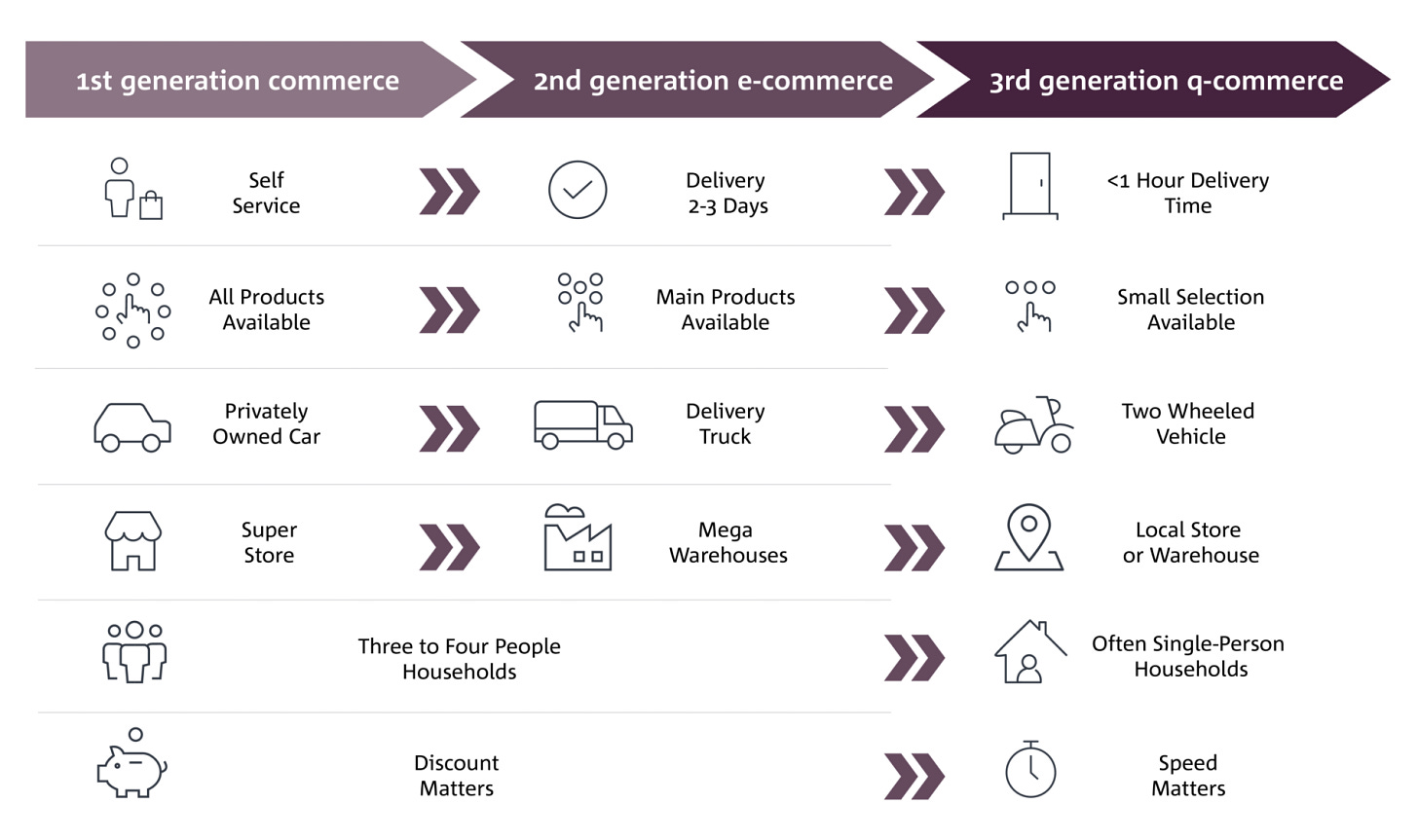
Quick Commerce, also known as Q-commerce, is a type of online retail service that focuses on delivering products to customers very quickly, usually within a short time frame like 10 minutes to an hour. Unlike traditional e-commerce, which might take a day or more to deliver, Q-commerce is all about speed and convenience. It typically offers a wide range of products, including groceries, snacks, household essentials, and even over-the-counter medicines, catering to immediate needs.
Historical Context and Evolution
Online shopping caught on in India in the early 2000s, with Flipkart and Amazon leading the charge. Delivery times ranged from several days to a week. By 2015, Grofers and BigBasket were delivering groceries within a couple of days, focusing on hyperlocal areas for faster service.
Then came startups like Dunzo and Swiggy Instamart, shaking things up with deliveries in hours or even minutes, and dominating the quick delivery scene.
They leveraged AI, ML, and data analytics to forecast demand and streamline routes, while electric bikes and drones cut down times even more.
The 2020 pandemic gave Q-commerce a massive boost, as homebound folks relied on it for speedy, contactless delivery of essentials.
Now, Q-commerce is a retail game-changer in India, with even traditional stores jumping on board to compete. The race for even quicker deliveries is on, thanks to relentless innovation and competition.
Market Size and Growth Rate
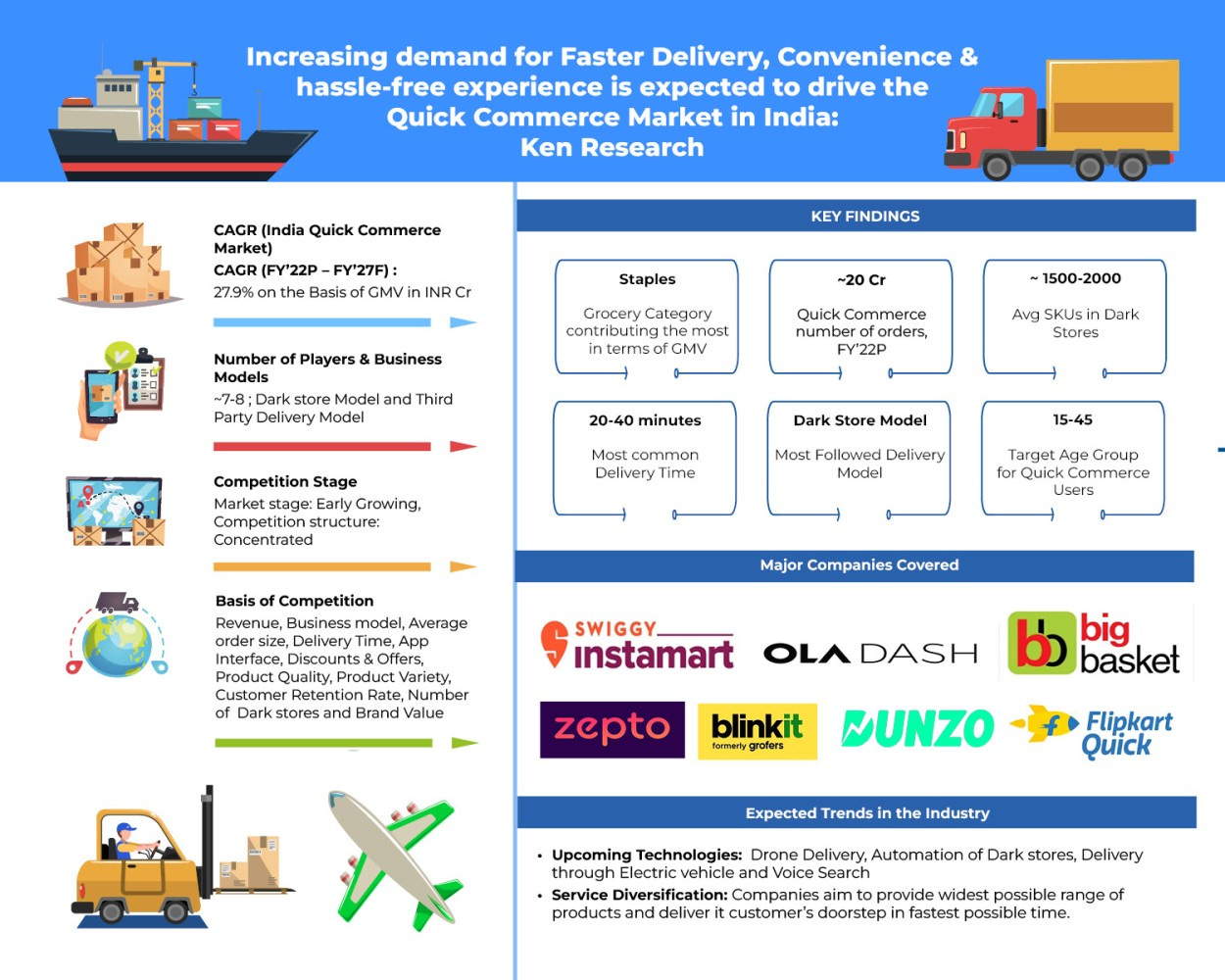
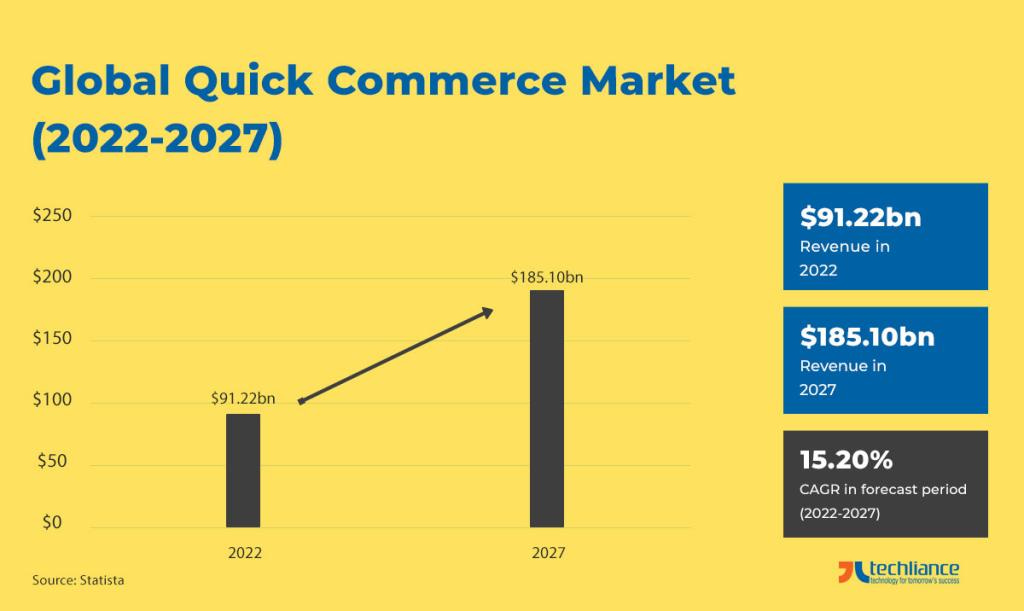
The Quick Commerce sector in India refers to businesses that focus on delivering goods rapidly, typically within 10 to 30 minutes of ordering. As of 2023, the market size of Q-commerce in India is estimated to be around $5 billion. This figure encompasses the revenue generated by various companies operating in this space, including startups and established players.
The sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by several factors:
Demand for Convenience: Consumers increasingly value convenience and quick access to goods, which Q-commerce fulfills by providing ultra-fast delivery times.
Urbanization: India's urban population is growing, and urban dwellers often have busy lifestyles that prioritize time-saving services like Q-commerce.
Technological Advancements: Advances in logistics technology and mobile app development have enabled Q-commerce companies to optimize delivery routes and offer efficient services.
The sector is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 25-30% over the next five years, indicating robust expansion potential.
Traditional E-commerce, Hyperlocal Delivery and Q-commerce
Traditional E-commerce:
Traditional e-commerce involves purchasing goods online and receiving them within a few days to a week, depending on the delivery speed chosen. Companies like Amazon, Flipkart, and others dominate this space. While traditional e-commerce offers a wide range of products and convenience of ordering from home, it typically cannot match the speed of Q-commerce.
Hyperlocal Delivery:
Hyperlocal delivery focuses on delivering goods from local stores to nearby customers within an hour or so. Services like Dunzo and Swiggy Genie fall into this category. Hyperlocal delivery is faster than traditional e-commerce but may not offer the immediacy of Q-commerce, which delivers goods within minutes.
Unique Selling Proposition of Q-commerce:
Q-commerce combines the convenience of traditional e-commerce with the speed of hyperlocal delivery. It caters to consumers who prioritize instant gratification and time efficiency. This unique selling proposition positions Q-commerce as a niche within the broader e-commerce and logistics ecosystem
Unique to Quick Commerce
Order Value:
In Q-commerce, the average order value tends to be lower compared to traditional e-commerce transactions. This is because Q-commerce often deals with daily essentials and small purchases that cater to immediate needs. Average order values typically range from INR 300 to INR 1000, reflecting the nature of goods commonly purchased through Q-commerce platforms.
Customer Demographics:
The primary customers of Q-commerce are young professionals, urban residents, and tech-savvy consumers. These demographics value convenience and time-saving solutions. They are comfortable using mobile apps to place orders and expect quick delivery of goods.
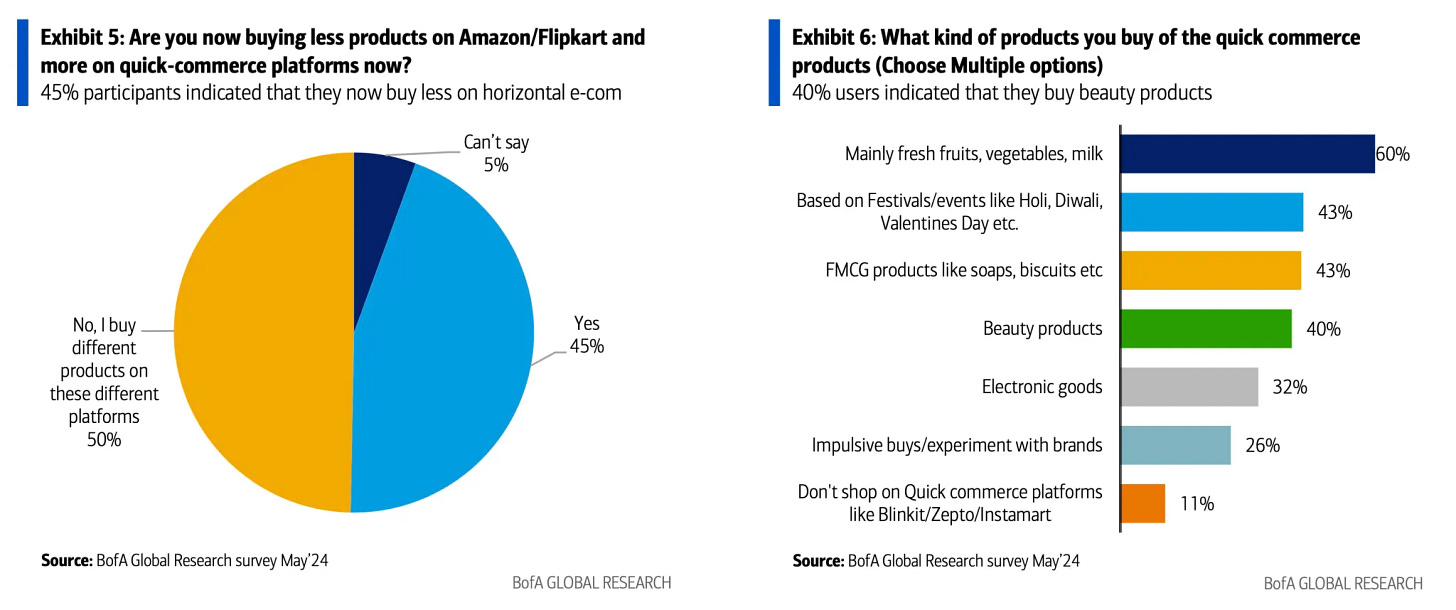
A recent Bernstein survey indicates that millennials, particularly those aged 18 to 35, show the highest adoption rates, with 60% of the 18 to 25 demographic favoring quick commerce platforms over traditional channels. Additionally, the adoption of digital channels extends to the 36 and older age group, with a preference for quick commerce exceeding 30%.
The distinct traits of Indian households add to the charm of quick commerce. Indian kitchens often have a larger variety of items in stock than Western ones, leading to more frequent shopping trips that local stores and quick commerce can handle more effectively than big retail chains. Plus, with the smaller storage space in many Indian homes, buying groceries in bulk every month isn't really doable, and since there's a preference for fresh food, quick commerce fits the bill perfectly.
Popular Product Categories:
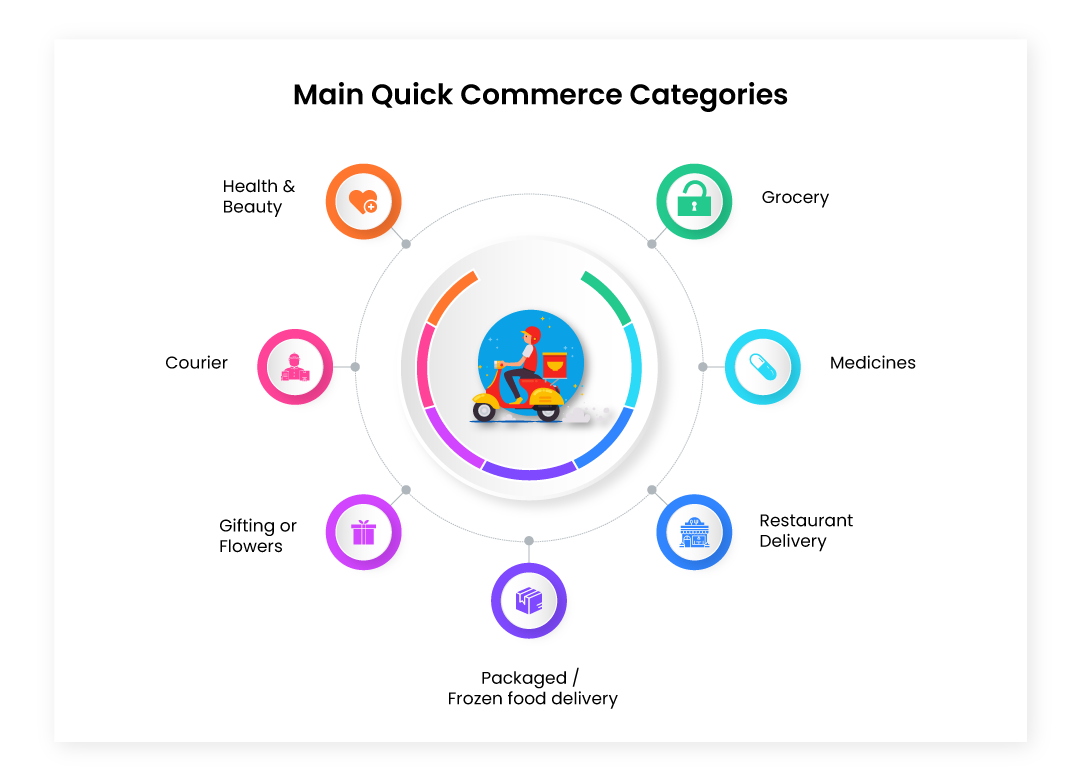
The most popular categories in Q-commerce include groceries, food items (like ready-to-eat meals and snacks), medicines, and daily essentials (such as toiletries and household items), gifts, etc. These categories cater to immediate consumption and everyday needs, making them ideal for rapid delivery services.
Bernstein reports that quick commerce platforms are able to offer products at prices 10% to 15% lower than traditional mom-and-pop stores while still preserving approximately 15% gross margins by eliminating intermediaries. Quick commerce dark stores have swiftly increased their SKU count from 2,000 to 6,000 and aim to boost it to between 10,000 and 12,000. Store managers note that these stores restock their inventory two to three times daily.
Quick commerce may not have to branch out from the grocery sector, which is already a massive market in India, worth over half a trillion dollars. However, their foray into electronics and fashion might be modest. Electronics account for 40% to 50% of total sales on platforms like Amazon and Flipkart, as per analysts. Should quick commerce tap into this segment successfully, it could become a formidable competitor to these e-commerce behemoths. Goldman Sachs has pegged the combined potential market for grocery and non-grocery items in the top 40-50 Indian cities at around $150 billion for quick commerce firms.
Regional Distribution and Major Cities
The growth of Q-commerce is not evenly distributed across India but concentrated in urban areas and major cities where demand for quick delivery services is highest. Key regions and cities driving the growth of Q-commerce include:
Mumbai: As India's financial capital with a fast-paced lifestyle, Mumbai has a significant demand for quick and convenient delivery services, including Q-commerce.
Delhi NCR (National Capital Region): This densely populated region, comprising New Delhi and its neighboring cities, represents a large market for Q-commerce due to its vast consumer base and urban lifestyle.
Bengaluru: Known as India's Silicon Valley, Bengaluru has a tech-savvy population that embraces innovative services like Q-commerce. The city's young demographic and high disposable income contribute to its appeal for Q-commerce companies.
Hyderabad and Chennai: Both cities are emerging markets for Q-commerce, driven by urbanization, increasing internet penetration, and a growing preference for online shopping among residents.
Major Players in India
Swiggy Instamart:
Overview: Swiggy Instamart is Swiggy's venture into quick commerce, focusing on delivering groceries and essentials within minutes.
Offerings: It provides a wide range of products including groceries, snacks, beverages, and household essentials.
Business Model: Leveraging Swiggy's existing network of delivery partners and infrastructure from its food delivery service.
Market Position: One of the leaders in the Q-commerce space due to Swiggy's strong brand presence and established user base from its food delivery service.
Blinkit (formerly Grofers):
Overview: Initially known as Grofers, Blinkit rebranded to focus on rapid delivery and efficiency.
Offerings: Offers groceries, fresh produce, household items, and personal care products.
Transformation: The rebranding aimed to enhance customer perception and streamline operations.
Competitive Edge: Known for competitive pricing and extensive product range, leveraging its experience in the grocery delivery market.
Zepto:
Overview: Zepto is a startup specializing in ultra-fast deliveries of groceries, medicines, and essentials.
Focus: Targets hyperlocal delivery, aiming for delivery times within minutes.
Strategy: Prioritizes customer convenience through quick service and a curated selection of products tailored to local preferences.
Market Position: Growing presence in select cities, appealing to urban customers looking for rapid delivery options.
Bigbasket Now:
Overview: Bigbasket Now is an initiative by Bigbasket, a major player in the online grocery segment.
Offerings: Provides quick delivery of groceries, fresh produce, and household items.
Integration: Integrated within Bigbasket's app ecosystem to provide seamless shopping and delivery experience.
Customer Base: Targets existing Bigbasket customers and new users seeking faster delivery options.
Market Share and Competitive Landscape
Market Share:
Leadership: Swiggy Instamart and Blinkit (Grofers) hold significant market shares due to their early entry and brand recognition.
Growth: Zepto and Bigbasket Now are gaining traction by focusing on specific niches within the quick commerce sector.
Regional Presence: Market share varies by region, with companies adapting strategies based on local preferences and logistics capabilities.
Competitive Landscape:
Speed and Efficiency: Companies compete on delivery times, aiming for faster and more reliable service.
Product Range: Offering a wide selection of products including groceries, fresh produce, snacks, beverages, and household essentials.
Customer Experience: Focus on customer satisfaction through seamless ordering, reliable delivery, and responsive customer service.
Technological Integration: Use of technology for efficient inventory management, route optimization, and customer communication.
Unique approaches of Indian Startups
Swiggy Instamart's Expansion:
Strategy: Leveraging Swiggy's existing food delivery infrastructure to quickly scale Instamart.
Impact: Expanded Swiggy's service offerings, increasing customer engagement and order frequency.
Learning: Integration of technology for efficient logistics and inventory management crucial for success.
Blinkit's Transformation:
Rebranding: Transition from Grofers to Blinkit to signify a shift towards rapid delivery and enhanced customer experience.
Operational Improvements: Streamlining processes to improve delivery times and order accuracy.
Market Response: Positive reception from customers and stakeholders following the rebranding.
Zepto's Localized Approach:
Market Niche: Targeting specific neighborhoods and urban areas for rapid delivery services.
Customer Engagement: Building customer loyalty through personalized service and curated product offerings.
Expansion Strategy: Gradual expansion into new cities based on market demand and operational readiness.
Business Models
Dark Stores and Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Dark Stores: Dark stores are essentially retail outlets that resemble traditional stores but are not open to the public. Instead, they operate solely for fulfilling online orders. The term "dark" refers to the fact that these stores are closed to customers and are dedicated fulfillment centers. They are strategically located in urban areas to reduce delivery times and costs. Dark stores carry a wide range of products similar to what you would find in a regular supermarket or retail store. They are equipped with technologies such as automated picking systems and inventory management tools to efficiently handle online orders and ensure quick dispatch to customers.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers: Micro-fulfillment centers are smaller-scale warehouses optimized for rapid order fulfillment. They are designed to be closer to consumers, typically located within urban areas or even embedded within existing retail spaces. These centers leverage automation technologies such as robots and AI to speed up the picking and packing process. By minimizing the distance between storage and delivery, micro-fulfillment centers enable quicker order processing and reduce the time it takes to get products to customers. They are particularly suited for handling high-volume orders from online platforms and meeting the demand for fast delivery services.
Aggregator Model vs. Direct-to-Consumer Model
Aggregator Model: In the aggregator model, a platform or company acts as an intermediary between consumers and multiple local businesses or service providers. This model is commonly seen in sectors like food delivery, where platforms partner with various restaurants to offer customers a wide selection of dining options through a single app or website. Aggregators consolidate offerings from different providers into a unified marketplace, providing consumers with convenience and choice. They handle logistics such as order processing, delivery, and customer support, thereby creating a seamless experience for users.
Direct-to-Consumer Model: The direct-to-consumer (DTC) model involves companies selling their products directly to consumers without intermediaries like retailers or wholesalers. This approach allows brands to establish a direct relationship with their customers, gaining valuable insights and feedback. DTC brands typically operate online through their own websites, mobile apps, or social media platforms. By bypassing traditional distribution channels, they have greater control over pricing, branding, and customer experience. DTC is particularly popular among digital-native brands offering niche products or personalized services.
Zomato works on aggregator model while BlinkIt works on D2C model.
Subscription-Based Services
Subscription-based services involve consumers paying a recurring fee at regular intervals to access goods or services. In the context of Quick Commerce, these services cater to recurring needs such as groceries, meal kits, personal care products, or entertainment content. Subscription models offer benefits to both consumers and businesses:
Consumer Benefits: Subscribers enjoy convenience, cost savings (through discounts or free shipping), and predictable deliveries of essential items.
Business Benefits: Companies benefit from predictable revenue streams, enhanced customer loyalty, and opportunities for cross-selling or upselling additional products.
Subscription-based Quick Commerce services often utilize data analytics to personalize offerings and optimize inventory management. They are designed to simplify the shopping experience and ensure regular engagement with customers.
Partnership and Collaboration Models
Partnership and collaboration models in Quick Commerce facilitate synergies between different businesses to enhance operational efficiency and expand market reach. Examples include:
Retailer and Tech Partner: Retailers collaborate with technology companies to integrate advanced features into their online platforms, such as AI-driven recommendation engines or efficient logistics solutions.
Supplier and Retailer: Suppliers partner with retailers to streamline supply chain processes, ensure consistent product availability, and optimize inventory levels based on consumer demand.
Platform and Service Provider: Platforms team up with service providers like logistics firms or payment processors to offer seamless transaction experiences and reliable delivery services.
These collaborative efforts enable businesses to leverage each other's strengths and resources. Partnerships in Quick Commerce are crucial for adapting to market dynamics, scaling operations, and meeting evolving consumer expectations efficiently.
Q-Commerce Technology
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Demand Forecasting
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing demand forecasting in Q-commerce by leveraging large datasets and complex algorithms to predict consumer behavior accurately. Here’s how they contribute:
Data Analysis: AI algorithms analyze historical sales data, customer behavior patterns, seasonal trends, and even external factors like weather conditions or social media trends.
Prediction Accuracy: By identifying patterns and correlations in data, AI can forecast demand with greater precision. For example, it can anticipate increased demand for winter clothing as temperatures drop or higher sales of outdoor furniture during summer months.
Real-Time Adjustments: Machine learning models continuously learn from new data inputs, enabling real-time adjustments to forecasts based on changing market conditions or unexpected events.
Inventory Optimization: Accurate demand forecasts help Q-commerce companies optimize inventory levels. They can stock sufficient quantities to meet anticipated demand without overstocking, thus minimizing costs and reducing the risk of stockouts.
Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management is critical in Q-commerce to ensure efficient operations and customer satisfaction. Advanced systems incorporate various technologies to streamline inventory control:
Real-Time Tracking: Utilizing IoT (Internet of Things) devices and RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags, inventory management systems provide real-time visibility into stock levels and locations across warehouses and stores.
Automated Reordering: AI-powered systems can automatically generate purchase orders based on predefined inventory thresholds and demand forecasts, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Demand-Driven Inventory: By integrating with demand forecasting models, inventory systems prioritize items based on anticipated sales, seasonal trends, and customer preferences.
Optimization Algorithms: Algorithms analyze data to optimize storage space, minimize holding costs, and ensure the availability of fast-moving items while managing slow-moving or perishable goods efficiently.
Last-Mile Delivery Solutions (e.g., Drones, Electric Vehicles)
Last-mile delivery is a crucial aspect of Q-commerce, focusing on delivering goods directly to customers swiftly and cost-effectively. Emerging technologies are transforming this phase:
Drone Delivery: Drones are being tested for delivering small packages over short distances. They offer quick deliveries and can navigate through traffic-congested urban areas, potentially reducing delivery times significantly.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs are increasingly used for last-mile deliveries due to their environmental benefits and lower operating costs compared to traditional fuel-powered vehicles. They help reduce carbon emissions and contribute to sustainability goals.
Route Optimization: AI algorithms optimize delivery routes in real-time based on factors like traffic conditions, delivery windows, and package sizes, ensuring efficient and timely deliveries.
Customer Convenience: These innovations enhance customer convenience by offering faster delivery options, real-time tracking of shipments, and flexible delivery schedules.
Mobile Apps and User Interface Innovations
Mobile apps serve as the primary interface for customers to interact with Q-commerce platforms. Innovations in UI design and functionality play a crucial role in enhancing user experience:
Intuitive Design: User interfaces are designed to be intuitive, making it easy for customers to browse products, place orders, and track deliveries seamlessly.
Personalization: AI-powered recommendation engines analyze customer data to provide personalized product suggestions, promotions, and offers tailored to individual preferences and past behavior.
One-Click Ordering: Simplified checkout processes with options like one-click ordering and stored payment information streamline the purchasing experience, reducing friction and increasing conversion rates.
Real-Time Updates: Mobile apps provide real-time updates on order status, shipment tracking, and notifications, keeping customers informed throughout the delivery process.
Data Analytics and Consumer Insights
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in Q-commerce by extracting valuable insights from vast amounts of data, enabling companies to make informed decisions:
Behavioral Analysis: Analyzing customer behavior data helps in understanding purchasing patterns, preferences, and trends, which informs product assortment decisions and marketing strategies.
Predictive Analytics: AI-driven predictive models forecast future trends and demand patterns, facilitating proactive inventory management and marketing campaign planning.
Segmentation: Customer segmentation based on demographics, purchasing behavior, and preferences allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized customer interactions.
Feedback Loop: Continuous analysis of customer feedback and reviews helps in improving products, services, and overall customer satisfaction, driving loyalty and repeat purchases.
Consumer Insights
Demographics of Quick Commerce Users
Quick Commerce refers to the trend of delivering essential goods and services quickly through digital platforms. In India, the demographic profile of QC users varies but generally includes:
Age: QC services are popular among a wide range of age groups, but there's a notable concentration among younger adults (18-35 years). This demographic is typically more tech-savvy and accustomed to using smartphones and digital platforms for various needs.
Urban Concentration: QC services are predominantly used in urban and metropolitan areas where population density is higher. Cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Hyderabad see significant usage due to their large populations and demand for fast-paced services.
Income Levels: While QC users come from diverse income backgrounds, middle to upper-income groups are more prevalent. These groups often have disposable income and are willing to pay for the convenience and speed offered by QC platforms.
Tech-Savviness: QC users are comfortable with technology and often prefer digital payment methods like wallets or UPI (Unified Payments Interface). This tech proficiency is crucial as QC platforms rely heavily on mobile apps and online transactions.
Purchasing Patterns and Preferences
Consumer behavior in the Quick Commerce sector is influenced by several factors:
Product Categories: Commonly purchased items through QC platforms include groceries, pharmaceuticals, ready-to-eat meals, personal care products, and even electronics. These are everyday essentials that consumers often need quickly.
Frequency of Purchases: QC users tend to make more frequent but smaller purchases compared to traditional shopping patterns. They value the ability to order items as needed, often on-demand, rather than doing bulk shopping.
Preference for Convenience: The primary attraction of QC services is convenience. Users appreciate the ability to order items with a few taps on their smartphones and have them delivered quickly, sometimes within minutes to a few hours.
Speed of Delivery: Swift delivery is a critical factor. QC platforms strive to provide fast delivery times to meet consumer expectations. The promise of quick turnaround from order to delivery is a key competitive advantage.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Consumer Behavior
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on consumer behavior within the Quick Commerce sector:
Acceleration of Online Shopping: With lockdowns and movement restrictions in place, there was a sharp increase in online shopping, including QC services. Consumers turned to digital platforms for their essential needs to avoid physical stores.
Safety and Hygiene Concerns: The pandemic heightened awareness about hygiene and safety. QC platforms responded by implementing contactless delivery options and stringent hygiene practices to reassure customers.
Expanded User Base: The pandemic accelerated the adoption of QC services beyond the usual demographic of tech-savvy urbanites. Older adults, families, and individuals previously hesitant to use digital platforms embraced QC for its convenience and safety.
Customer Retention Strategies
To retain customers and foster loyalty, QC platforms employ various strategies:
Personalization: Tailoring the user experience based on past purchases and preferences. This could include personalized recommendations and promotions sent through app notifications or email.
Loyalty Programs: Offering rewards such as discounts, cashback, or exclusive offers for frequent users. Loyalty programs incentivize repeat purchases and encourage customers to stick with a particular QC platform.
Service Quality: Ensuring reliable and timely delivery is crucial. QC platforms invest in logistics infrastructure and operational efficiency to maintain high service standards. Any lapses in delivery times or service quality can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Feedback Mechanisms: Actively seeking feedback from customers through ratings, reviews, and surveys. This helps QC platforms identify areas for improvement and address customer concerns promptly.
User Feedback and Reviews
User feedback and reviews are integral to the success of QC platforms:
Service Improvement: Feedback helps QC platforms refine their operations. For example, if users consistently report issues with delivery times or product quality, the platform can take corrective actions to enhance service levels.
Trust Building: Positive reviews and high ratings build trust among potential customers. Prospective users often rely on reviews from existing customers to gauge the reliability and quality of a QC platform before making a purchase.
Transparency and Accountability: Addressing negative feedback publicly demonstrates transparency and a commitment to customer satisfaction. QC platforms that respond proactively to criticism and resolve issues promptly can enhance their reputation and retain customer trust.
Challenges in Quick Commerce
Operational Challenges:
Logistics: Q-commerce relies on the ability to deliver products quickly, often within hours of the order being placed. This requires efficient logistics networks that can handle rapid fulfillment and last-mile delivery. In India, the logistics infrastructure varies widely across regions, with challenges such as traffic congestion, inadequate road networks, and varying levels of technology adoption by logistics providers.
Supply Chain Management: Effective supply chain management is crucial for Q-commerce companies to maintain high service levels and manage costs. This includes sourcing products efficiently, managing inventory across multiple locations, and optimizing fulfillment processes to minimize delivery times. In India, managing supply chains can be complex due to diverse supplier bases, unpredictable demand fluctuations, and regulatory requirements for inventory management.
High Customer Acquisition Costs:
Acquiring customers in the Q-commerce sector can be costly due to intense competition and the need to attract customers away from established competitors. Costs include marketing expenditures across digital platforms, offering discounts and promotions to incentivize first-time purchases, and investing in customer service to retain loyalty. The cost-effectiveness of customer acquisition strategies is critical for Q-commerce companies to achieve sustainable growth.
Regulatory and Legal Issues:
Q-commerce companies must navigate a complex regulatory environment in India. This includes compliance with e-commerce regulations such as data protection laws (e.g., Personal Data Protection Bill), consumer protection laws (e.g., Consumer Protection Act), and taxation rules (e.g., GST). Ensuring compliance with these regulations adds operational overhead and may require ongoing legal support to interpret and adapt to evolving laws.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns:
The rapid growth of Q-commerce has raised concerns about its environmental impact, particularly in terms of carbon emissions from delivery vehicles and packaging waste. Sustainable practices such as optimizing delivery routes to reduce mileage, using eco-friendly packaging materials, and exploring alternative energy sources for delivery fleets are becoming increasingly important. Balancing speed and convenience with environmental responsibility is a significant challenge for Q-commerce companies aiming to minimize their carbon footprint.
Competition and Market Saturation:
The Q-commerce sector in India is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. This intense competition can lead to price wars and reduced profit margins as companies strive to attract and retain customers. Market saturation in urban areas poses challenges for new entrants, requiring differentiation through innovative services, superior customer experiences, or niche market targeting to gain traction and sustain growth.
Opportunities in Quick Commerce
Untapped markets and regions:
Quick Commerce, or Q-commerce, focuses on delivering goods rapidly, often within hours of an order being placed online. In India, while major cities might have established delivery services, there are numerous smaller towns and neighborhoods within cities that lack efficient and quick delivery options. These areas represent untapped markets where there is demand for fast and reliable delivery services.
Opportunity: Companies in the Q-commerce sector can expand their operations into these underserved regions. By doing so, they can capture a significant portion of the market that currently lacks access to quick delivery services. This expansion not only broadens their customer base but also establishes their presence in areas where competition may be less intense compared to saturated urban markets.
Product diversification (e.g., groceries, pharmaceuticals, electronics):
Q-commerce isn't restricted to delivering just one type of product. It encompasses a wide array of goods including groceries, pharmaceuticals (medicines), electronics, personal care items, and more. This diversification allows Q-commerce companies to cater to diverse consumer needs, ranging from daily essentials to specialized products.
Opportunity: By offering a broad range of products, Q-commerce businesses can increase their relevance and appeal to a larger customer base. Consumers today value convenience and prefer platforms that allow them to fulfill multiple needs in one place. Therefore, integrating various product categories enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Integration with other services (e.g., fintech, telemedicine):
In the evolving landscape of digital commerce, integrating complementary services such as fintech (financial technology) and telemedicine presents significant opportunities. Fintech collaborations can streamline payment processes, offering seamless and secure transactions. Telemedicine partnerships enable Q-commerce companies to deliver pharmaceuticals quickly to patients following medical consultations.
Opportunity: Collaborating with fintech and telemedicine providers enhances the overall customer experience by making transactions smoother and ensuring timely access to essential healthcare products. This integration also positions Q-commerce businesses at the forefront of digital innovation, catering to the growing demand for integrated digital services.
Enhancing customer experience through personalization:
Personalization involves tailoring the shopping experience to individual customer preferences and behaviors. Q-commerce companies can leverage data analytics and AI-driven technologies to understand customer preferences, past purchase behavior, and browsing history. This enables them to recommend relevant products and promotions, thereby enhancing the overall shopping experience.
Opportunity: By investing in personalization strategies, Q-commerce businesses can differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Personalized recommendations increase customer satisfaction and engagement, leading to higher conversion rates and repeat purchases. Moreover, a personalized shopping experience fosters brand loyalty as customers feel understood and valued by the platform.
Leveraging social media and digital marketing:
In today's digital age, social media platforms and digital marketing channels play a crucial role in reaching and engaging with consumers. Q-commerce companies can utilize social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to promote their products, interact with customers, and build brand awareness. Additionally, targeted digital marketing campaigns can reach specific demographics based on consumer preferences and behaviors.
Opportunity: Effective use of social media and digital marketing enables Q-commerce businesses to expand their reach and attract new customers. These platforms offer tools for precise targeting, allowing businesses to optimize their marketing spend and achieve higher ROI. Engaging content, influencer collaborations, and promotions can help Q-commerce companies build a strong online presence and drive traffic to their platforms.
Quick Commerce Finance
Funding and Investment Trends:
Funding and investment are crucial for Q-commerce companies to grow and expand their operations. In India, the Q-commerce sector has been attracting significant investments from various sources, including venture capitalists, private equity firms, and sometimes even large corporations looking to diversify.
Venture Capitalists (VCs): These are firms or individuals that invest in startups and early-stage companies with high growth potential. In the Q-commerce sector, VCs are particularly interested due to the rapid adoption of online shopping and the increasing demand for quick delivery of goods.
Private Equity (PE) Firms: These firms typically invest in more mature companies that are looking to expand or restructure. In Q-commerce, PE firms might invest in companies that have already established a customer base and operational infrastructure but need capital to scale up.
Corporate Investments: Established companies, especially those in related industries like e-commerce or logistics, may invest in Q-commerce startups to gain strategic advantages such as access to new technologies, markets, or customer segments.
Investment Trends in India: Q-commerce startups in India have seen a surge in funding primarily because of the country's rapidly growing middle class, increasing internet penetration, and changing consumer preferences towards convenience. Investors are attracted to the potential for high returns as these companies aim to capitalize on the trend of quick and efficient delivery of essential items.
Revenue Models
Revenue models in Q-commerce determine how companies generate income from their operations. In India, Q-commerce companies typically employ the following revenue strategies:
Delivery Fees: Charging customers a fee for delivering their orders quickly. This fee can vary based on factors like distance, time of day, and urgency of delivery.
Subscription Services: Offering subscription plans where customers pay a recurring fee in exchange for benefits such as free or discounted deliveries, exclusive discounts, or priority service.
Product Markups: Some Q-commerce platforms may charge slightly higher prices for products compared to traditional retail to cover the costs of fast delivery and convenience.
Advertising and Partnerships: Generating revenue through advertising on their platforms or partnering with brands to promote products.
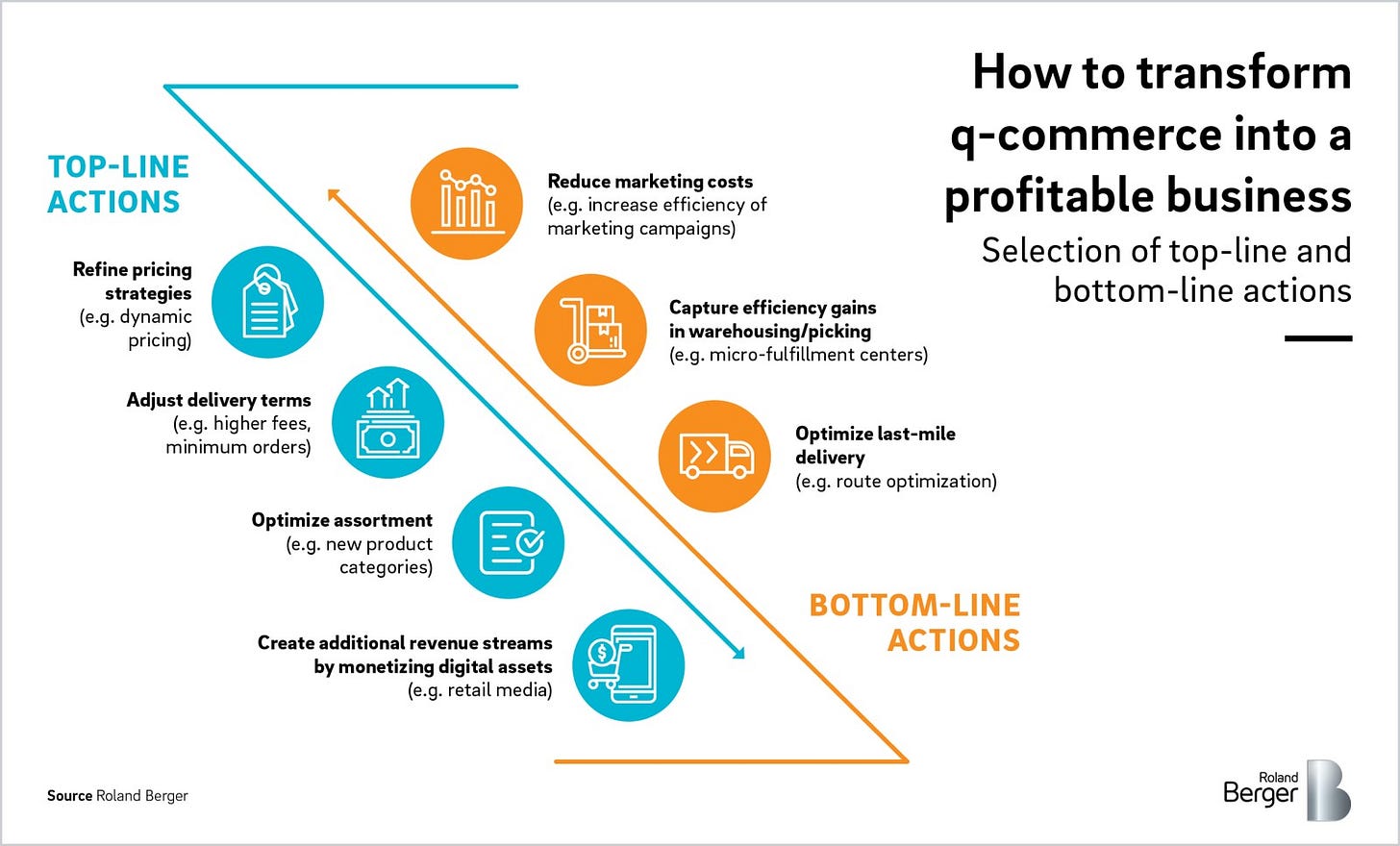
Profitability
Achieving profitability in Q-commerce can be challenging due to high operational costs, including logistics, technology infrastructure, and customer acquisition. Profitability is typically measured by ensuring that revenue from sales and services exceeds these costs over the long term. Q-commerce companies in India focus on achieving profitability through various strategies:
Operational Efficiency: Optimizing delivery routes, inventory management, and warehouse operations to reduce costs and improve delivery times.
Scale and Volume: Increasing the number of orders fulfilled per day to spread fixed costs over a larger base and improve margins.
Customer Retention: Encouraging repeat purchases through loyalty programs, personalized offers, and exceptional customer service to increase lifetime customer value.
Cost Structure
Cost structure in Q-commerce encompasses the various expenses incurred in running the business. In India, key components of cost structure include:
Logistics Costs: Expenses related to transporting goods from warehouses or stores to customers' locations. This includes fuel costs, vehicle maintenance, and labor costs for delivery personnel.
Technology Infrastructure: Investments in technology platforms, mobile apps, and backend systems to manage orders, inventory, and customer relationships efficiently.
Marketing and Customer Acquisition: Costs associated with marketing campaigns, promotions, and discounts to attract and retain customers.
Employee Expenses: Salaries, benefits, and training costs for warehouse staff, delivery personnel, customer service representatives, and management.
Pricing Strategies
Pricing Strategies: Q-commerce companies in India employ various pricing strategies to attract customers while ensuring profitability:
Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on demand, supply, time of day, or customer location. This helps maximize revenue during peak periods and optimize inventory turnover.
Subscription Models: Offering subscription plans that provide customers with predictable costs and benefits like free deliveries or discounts in exchange for a recurring fee.
Promotions and Discounts: Running limited-time offers, seasonal sales, or discounts on bulk orders to stimulate demand and increase sales volume.
Competitive Pricing: Monitoring competitors' pricing strategies to stay competitive while maintaining reasonable profit margins.
Mergers and Acquisitions:
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) play a significant role in shaping the Q-commerce landscape in India:
Market Consolidation: Larger companies may acquire smaller competitors to eliminate competition and strengthen their market position.
Access to Technology: Acquiring startups with innovative technologies or proprietary algorithms can help larger companies enhance their service offerings and improve operational efficiency.
Geographical Expansion: Acquiring companies with a strong presence in different regions allows Q-commerce firms to quickly expand their delivery network and customer base.
Diversification: M&A activities can help Q-commerce companies diversify their product offerings or enter new market segments to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging trends.
Financial Synergies: Mergers can lead to cost savings through economies of scale, shared resources, and streamlined operations, which can improve profitability.
Growth Projections and Market Forecasts
Q-Commerce, also known as ultra-fast delivery or on-demand delivery, is a rapidly growing segment within the broader e-commerce industry. It focuses on delivering goods to consumers within a very short timeframe, often within hours or even minutes of placing an order. This sector is gaining traction due to several key factors:
Increasing Internet Penetration and Smartphone Use:
India has seen a significant increase in internet penetration, driven by affordable smartphones and data plans. This has expanded the customer base for online shopping, including Q-Commerce.
According to Statista, India had over 624 million internet users as of 2021, and this number is expected to grow further. Similarly, smartphone penetration has grown, with more than 760 million smartphone users in the country.
Changing Lifestyles and Demand for Convenience:
Urbanization, busy lifestyles, and a rising middle class are driving the demand for convenience in shopping.
Consumers increasingly value time-saving solutions, preferring quick delivery of groceries, medicines, and other daily essentials over traditional shopping methods.
Market Potential and Investment:
Analysts predict substantial growth in the Q-Commerce sector in India. For example, RedSeer Consulting estimated that the hyperlocal delivery segment (a subset of Q-Commerce) could grow to $4.3 billion by 2025.
Investments from venture capitalists and e-commerce giants like Amazon, Flipkart, and BigBasket indicate confidence in the sector's growth potential.
Expansion of Delivery Networks:
Companies are investing in expanding their delivery networks and optimizing logistics to meet customer expectations.
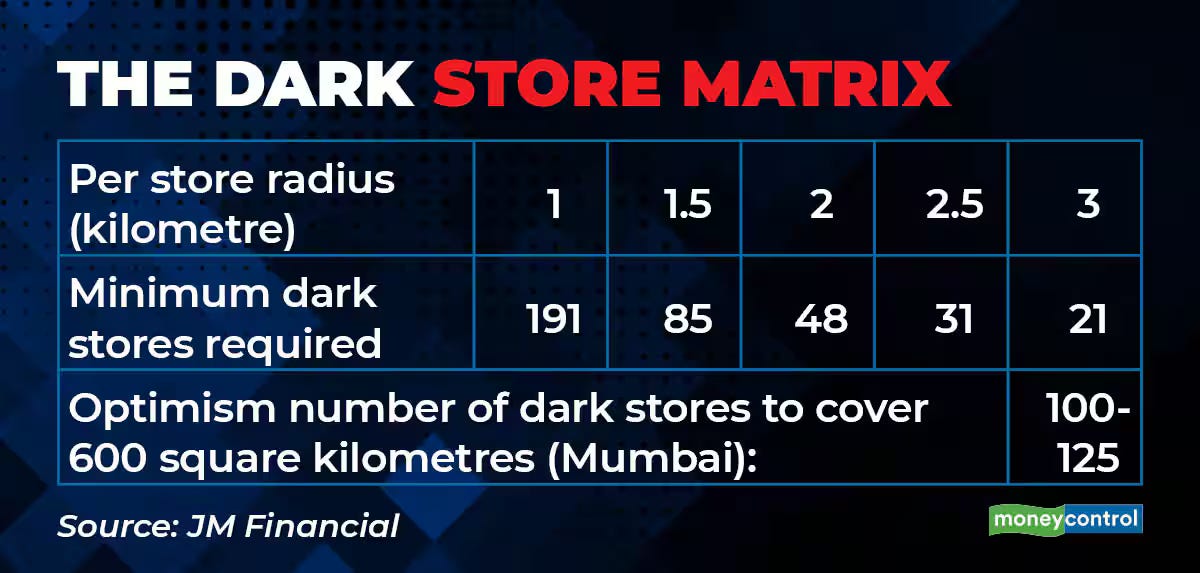
This includes setting up warehouses or dark stores closer to residential areas to enable faster deliveries.
Changing Consumer Expectations:
Consumers' expectations are evolving, driven by their experiences with digital services and e-commerce platforms:
Demand for Speed and Convenience:
Consumers expect faster delivery times, often within a few hours of placing an order. This trend is especially prominent in urban areas where time is a critical factor.
Companies like Dunzo, Swiggy Genie, and Flipkart Quick are leveraging this demand by offering hyper-local deliveries.
Personalization and Customer Experience:
Personalized recommendations based on past purchases and browsing behavior enhance customer satisfaction and encourage repeat purchases.
Seamless and intuitive user interfaces on mobile apps and websites simplify the ordering process.
Trust and Reliability:
Consumers prioritize reliability in delivery services. They expect accurate tracking information, timely updates, and responsive customer support.
Trust in the quality and freshness of goods, especially for perishable items like groceries and medicines, is crucial.
Government Policies and Support:
Government policies and regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the operational landscape for Q-Commerce companies:
Regulatory Framework:
Clear regulations on data privacy, cybersecurity, and consumer protection are essential for building trust among consumers.
Policies that support digital infrastructure development, such as broadband expansion and digital payment systems, are critical for the sector's growth.
Ease of Doing Business:
Streamlined processes for business registration, licenses, and permits reduce administrative burdens for startups and encourage entrepreneurship.
Initiatives promoting logistics infrastructure development, such as dedicated freight corridors and cold chain facilities, support efficient supply chain management.
Taxation and Incentives:
Tax incentives and subsidies for investments in technology and infrastructure can stimulate innovation and growth in the Q-Commerce sector.
Policies that foster competition and prevent monopolistic practices ensure a level playing field for businesses.
Impact of Global Trends on the Indian Market:
Global trends and practices influence the evolution of Q-Commerce in India:
Adoption of Best Practices:
Indian companies benchmark against global leaders in e-commerce and logistics to improve operational efficiency and customer service.
Partnerships and collaborations with international firms bring global expertise and technology to the Indian market.
Investment and Partnerships:
Global investment in Indian startups and tech firms, particularly in e-commerce and logistics, accelerates innovation and expansion.
Strategic partnerships between Indian and international companies enhance market reach and capabilities in supply chain management.
Technological Innovation:
Advancements in e-commerce technologies, such as AI, ML, blockchain, and IoT, are adopted globally and localized for the Indian market.
Cross-border e-commerce initiatives facilitate trade and enable Indian consumers to access a wider range of products.
Detailed Analysis of Successful Quick Commerce Companies
Quick Commerce (QC) companies in India have revolutionized how essentials like groceries and household items are delivered to consumers. Successful companies in this sector have typically mastered several key elements:
Efficient Logistics Networks: Companies like Swiggy Instamart and Dunzo have established robust logistics networks. They partner with local stores and leverage a fleet of delivery agents to ensure quick order fulfillment. This involves strategically locating fulfillment centers and optimizing delivery routes to minimize delivery times.
Technology Integration: Successful QC companies heavily invest in technology. They use algorithms and machine learning to predict demand patterns, manage inventory efficiently, and optimize delivery routes. This technology also enhances the user experience through intuitive apps and interfaces that make ordering fast and simple.
Customer Experience: Providing a seamless customer experience is crucial. Successful companies focus on aspects such as accurate order fulfillment, timely delivery (often within 15-30 minutes), and responsive customer support. They often offer a wide range of products to cater to diverse consumer needs.
Adaptability and Scalability: Companies that scale effectively often start in urban centers and gradually expand their reach. They adapt their strategies based on local market dynamics and consumer behaviors. This adaptability includes diversifying product offerings based on regional preferences and refining operations to improve efficiency over time.
Financial Sustainability: Achieving profitability remains a challenge in the QC sector due to high operational costs, including logistics, technology infrastructure, and marketing. Successful companies often secure significant investment initially to build their infrastructure and scale operations before focusing on achieving profitability through increased order volumes and operational efficiencies.
Lessons Learned from Failed Ventures
Not all ventures in the Quick Commerce sector have succeeded. Several factors contribute to failures:
Poor Operational Execution: Some ventures fail due to inadequate management of logistics and supply chain operations. This can lead to delays in order fulfillment, inconsistent service quality, and increased operational costs.
Lack of Technological Integration: Companies that do not invest sufficiently in technology struggle to optimize operations and meet customer expectations for speed and reliability. This includes inventory management systems, demand forecasting tools, and efficient routing algorithms.
Market Fit and Consumer Understanding: Ventures that do not deeply understand local consumer preferences and behaviors may struggle to attract and retain customers. Understanding which products are in demand and tailoring offerings accordingly is crucial.
Financial Mismanagement: High operational costs combined with aggressive expansion strategies can strain finances. Companies must balance growth ambitions with financial sustainability to avoid running out of capital.
Competition and Pricing Strategy: Intense competition in the QC sector can lead to price wars and thin profit margins. Companies must develop a pricing strategy that balances affordability with profitability while considering consumer willingness to pay.
Summary of Key Findings
Market Growth:
The quick commerce sector in India has experienced rapid growth primarily due to increasing urbanization, changing consumer lifestyles, and the convenience offered by fast delivery services. Urban areas, where people often have hectic schedules, find quick commerce services particularly appealing as they can receive essential items within an hour or two of placing an order.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of online shopping and quick commerce as people sought to minimize physical contact and trips to stores.
Consumer Behavior:
Consumers are increasingly preferring to purchase daily essentials online due to convenience, time-saving benefits, and the availability of a wide range of products. The ability to shop anytime, anywhere via smartphones has significantly influenced buying patterns.
Factors such as reliable delivery timelines, product quality assurance, and hassle-free return policies are crucial in shaping consumer trust and loyalty towards quick commerce platforms.
Competition:
The quick commerce sector in India is highly competitive, characterized by the presence of established e-commerce giants like Amazon and Flipkart, as well as specialized startups such as Grofers, BigBasket, and Dunzo. These players are constantly innovating to differentiate themselves and capture market share.
Competition has led to improvements in service levels, technological advancements in delivery logistics, and a broader range of product offerings to cater to diverse consumer needs and preferences.
Logistics Challenges:
Efficient logistics and supply chain management are critical in quick commerce due to the need for timely deliveries and maintaining product freshness.
Challenges include optimizing route planning, managing inventory to prevent stockouts, ensuring last-mile delivery efficiency, and handling returns effectively.
Companies invest in advanced logistics technologies, such as real-time tracking systems, AI-powered demand forecasting, and warehouse automation, to streamline operations and enhance delivery reliability.
Regulatory Environment:
The regulatory landscape in India impacts the operations of quick commerce platforms, particularly in terms of online retail regulations, taxation, and compliance with consumer protection laws.
Adherence to local laws and regulations governing e-commerce, data privacy, food safety (for groceries and perishables), and transport logistics is essential to avoid legal complications and ensure sustainable growth.
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
Enhance Delivery Infrastructure:
Stakeholders should invest in developing a robust delivery infrastructure encompassing warehouses, fulfillment centers, and a network of delivery personnel or partners.
Adopting advanced logistics management systems that facilitate real-time tracking, route optimization, and efficient inventory management can significantly improve delivery speed and reliability.
Customer Experience:
Improving customer experience involves creating user-friendly interfaces for mobile apps and websites, offering personalized recommendations based on past purchases and preferences, and providing reliable customer support channels.
Quick response times for queries, easy order tracking, and transparent communication regarding delivery updates are critical to enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Partnerships and Alliances:
Forming strategic partnerships with local vendors, wholesalers, and technology providers can strengthen the supply chain and expand product offerings.
Collaborations with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) and last-mile delivery specialists can help mitigate logistics challenges and extend delivery reach to underserved areas.
Regulatory Compliance:
Stakeholders must stay informed about evolving regulatory requirements and ensure compliance to avoid legal repercussions that could disrupt operations.
This includes adhering to tax regulations, data protection laws, and local regulations specific to the transportation and delivery of goods.
Innovation:
Continuous innovation is essential to stay ahead in the competitive quick commerce landscape. This includes exploring new technologies such as drones or autonomous vehicles for delivery, implementing AI-driven predictive analytics for demand forecasting, and experimenting with sustainable packaging solutions.
Innovations aimed at reducing delivery times, improving operational efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact can enhance competitiveness and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
SOMEONE CAN BENEFIT FROM IT
If you find this post helpful, we would be grateful if you could take a moment to share it with others who might benefit from it. Your kindness and support mean a lot to us.
DYNAMIC CONTENT
No one knows how deep a rabbit hole can go.
All our posts are regularly updated as soon as new information becomes available. We also keep note of the questions asked by our readers and add their answers to the article. So, stay curious and ask questions in the comments.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Hey everyone, I'm Garvit Sahdev 😎. I'm on a mission to gain a deeper understanding of the world, and to develop solutions that can trigger significant global change.
My curiosities span various domains including food, business theories, material science, market size calculations, economics, politics, and sports, etc. 🧐
Professionally, I have a diverse background spanning startups, consulting, policy development, market research, system building, ISO, colour physics, nanomaterial synthesis, textile chemistry, etc. 🐘
Thanks for reading The Thoughtful Tangle! Subscribe to continue reading deeply researched stories about the interesting concepts that shape our world. ❤️